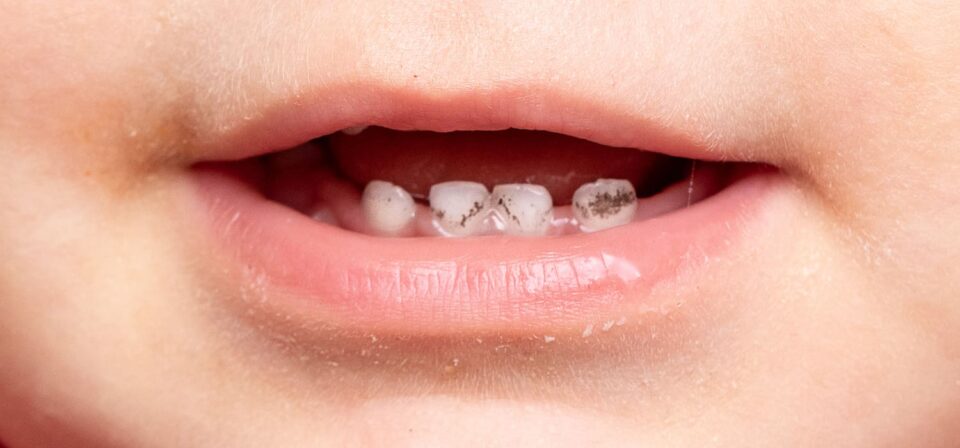
Tooth decay is when the hard outer layer of a tooth, called enamel, begins to break down. This can lead to cavities, which are holes in the teeth. If left untreated, cavities can grow deeper and reach the nerves inside the tooth, causing pain and sensitivity.
What Causes Tooth Decay in Children?
Tooth decay happens because of bacteria in the mouth. When children eat foods with sugars or starches, like milk, soda, candy, cake, raisins, fruit juice, cereals, or bread, these bacteria turn the food into acids. Visiting a dentist near me can help detect and prevent these issues early. The acids mix with saliva and form a sticky layer on the teeth called plaque. Over time, the acids in plaque wear down the enamel and create cavities.
Which Children Are at Risk?
All children have bacteria in their mouths, so everyone is at risk for tooth decay. Some factors can increase the risk:
- High levels of cavity-causing bacteria
- Eating too many sugary or starchy foods
- Drinking water with little or no fluoride
- Poor oral hygiene
- Low saliva flow
Symptoms of Tooth Decay
Tooth decay may appear differently in each child, but common signs include:
- White spots on teeth, which show early enamel damage and may cause sensitivity
- Light brown spots indicating the start of a cavity
- Dark brown or black spots as the cavity gets deeper
Some children may not feel any pain at first. Symptoms, when they appear, can include:
- Pain near the affected tooth
- Sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods
Diagnosis and Treatment
Dentists can diagnose tooth decay by examining the child’s mouth, taking a dental history, and using X-rays. Treatment depends on the child’s age, oral health, and the severity of the decay.
Early decay can sometimes be treated without fillings using:
- Plaque removal and cleaning
- Fluoride treatments
- Dental sealants
If the cavity is larger, the decayed part of the tooth is removed and replaced with a filling. Fillings can be:
- Direct restorations: Placed in a single visit and can be made from tooth-colored materials or metals
- Indirect restorations: Made in a lab, including crowns, veneers, or inlays, often requiring multiple visits
Preventing Tooth Decay in Children
Parents can help prevent decay with these steps:
- Begin brushing when the first tooth appears, using a small amount of fluoride toothpaste
- Brush twice a day for two minutes and floss daily after age two
- Limit sugary or sticky foods and drinks
- Give only water in bedtime bottles
- Ask your dentist about fluoride supplements, sealants, or fluoride varnish
- Schedule dental checkups every six months
Key Points
- Tooth decay is the destruction of enamel and can lead to cavities
- Bacteria in the mouth and sugary foods cause decay
- Poor oral hygiene increases the risk
- Dentists diagnose decay with exams and X-rays
- Treatment may involve cleaning, fluoride, sealants, or fillings
By following proper oral care habits and visiting the dentist regularly, you can help protect your child’s teeth from decay and keep their smile healthy.